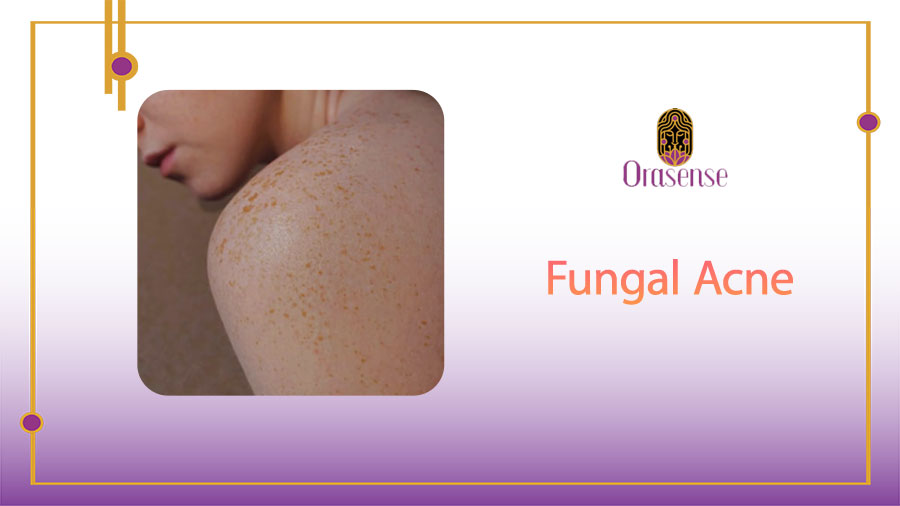
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. However, there is a type of acne that is not as well-known – fungal acne. It also known as pityrosporum folliculitis, is a type of acne that is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin.
Fungal acne is often confused with traditional acne, as the symptoms are similar. However, the treatment for this disorder is different from traditional acne. This kind of acne appears as small, red bumps on the skin, which can be itchy and uncomfortable.
If left untreated, fungal acne can spread and become more severe. Understanding the causes and solutions for fungal acne is crucial in preventing and treating this condition.
Table of contents
- What is Fungal Acne and How is it Different from Traditional Acne?
- Understanding the Causes of Fungal Acne
- How to Diagnose Fungal Acne
- Treating Fungal Acne – Over-the-Counter Options
- Prescription Treatments for Fungal Acne
- Natural Remedies for Fungal Acne
- Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Fungal Acne
- Conclusion
What is Fungal Acne and How is it Different from Traditional Acne?
It is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin, specifically the yeast Malassezia. Traditional acne, on the other hand, is caused by a combination of factors, including excess oil production, clogged pores, and bacteria. Check our article about gets rid of acne for more details about traditional acne treatment.
Fungal acne appears as small, red bumps on the skin, which can be itchy. Traditional acne can appear as whiteheads, blackheads, or pimples. It is most commonly found on the chest, back, and upper arms, while traditional acne can occur on the face, chest, back, and shoulders.
The treatment for fungal acne is different from traditional acne. Traditional acne is treated with topical or oral medications, while fungal acne is treated with antifungal medications.
Understanding the Causes of Fungal Acne
The primary cause of this acne is an overgrowth of yeast on the skin. This yeast, Malassezia, is commonly found on the skin and does not cause any problems in most people. However, in some individuals, an overgrowth of this yeast can occur, leading to the development of fungal acne.
Certain factors can trigger an overgrowth of Malassezia, including:
1. Humidity and Heat
Humidity and heat can increase the likelihood of developing fungal acne by creating an environment that is favorable for the growth of yeast. When the air is humid, it can trap moisture on the skin, providing an ideal breeding ground for the yeast that causes this kind of acne. Similarly, when the skin is exposed to heat, it can become sweaty, which can also create a moist environment that promotes yeast growth.
2. Sweating
Sweating and heat can also contribute to the development of fungal acne by creating an environment that is warm and moist, which can promote the growth of yeast on the skin. When the skin is exposed to heat, it can become sweaty, and this sweat can mix with bacteria and dead skin cells, creating a perfect environment for yeast to thrive.
3. Use of Antibiotics
The use of antibiotics can actually worsen fungal acne, as they can disrupt the balance of bacteria on the skin and create an environment that is more conducive to the growth of yeast. Antibiotics can also weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off fungal infections. Therefore, it is important to avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics and to seek alternative treatments for bacterial acne if possible. If antibiotics are necessary, it is important to use them only as directed and to follow up with probiotics or other measures to restore the balance of bacteria on the skin.
4. Use of Oily Skincare Products
Oily skincare products can clog pores and create a favorable environment for the growth of yeast on the skin.
How to Diagnose Fungal Acne

Diagnosing this kind of acne can be challenging, as the symptoms are similar to traditional acne. However, there are some clues that can help differentiate between the two.
Fungal acne is most commonly found on the chest, back, and upper arms, while traditional acne can occur on the face, chest, back, and shoulders. This type of acne appears as small, red bumps on the skin, which can be itchy and uncomfortable. Traditional acne can appear as whiteheads, blackheads, or pimples.
A dermatologist can diagnose fungal acne through a skin biopsy or by examining the affected area. The dermatologist may also take a sample of the affected skin and examine it under a microscope to confirm the presence of Malassezia.
Treating Fungal Acne – Over-the-Counter Options
Mild cases of this acne can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal products. These products contain ingredients like ketoconazole, which can help reduce the overgrowth of Malassezia on the skin.
Some popular over-the-counter antifungal products include:
1. Nizoral Shampoo
Nizoral shampoo contains ketoconazole and is commonly used to treat dandruff. To use, lather the shampoo on the affected area and let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing off.
2. Lotrimin Cream
Lotrimin cream contains clotrimazole and is commonly used to treat athlete’s foot and jock itch. However, it can also be used to treat fungal acne. To use, apply a thin layer of the cream to the affected area twice a day.
3. Selsun Blue Shampoo
Selsun Blue shampoo contains selenium sulfide and is commonly used to treat dandruff. To use, lather the shampoo on the affected area and let it sit for a few minutes before rinsing off.
Prescription Treatments for Fungal Acne
For more severe cases of fungal acne, prescription medications may be necessary. These medications are typically prescribed by a dermatologist and include:
1. Topical Antifungal Medications
Topical antifungal medications, such as ciclopirox and efinaconazole, can be applied directly to the affected area to reduce the overgrowth of Malassezia.
2. Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal medications, such as fluconazole and itraconazole, can be taken to reduce the overgrowth of Malassezia. These medications are typically prescribed for more severe cases of fungal acne.
Natural Remedies for Fungal Acne

In addition to over-the-counter and prescription treatments, there are also some natural remedies that can help reduce the symptoms of fungal acne. These remedies include:
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antifungal properties and can help reduce the overgrowth of Malassezia on the skin. To use, apply a few drops of tea tree oil to a cotton ball and dab it onto the affected area.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antifungal properties and can help reduce the overgrowth of Malassezia on the skin. To use, dilute apple cider vinegar with water and apply it to the affected area with a cotton ball.
3. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the redness and inflammation associated with fungal acne. To use, apply a thin layer of aloe vera gel to the affected area.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Fungal Acne
Making some lifestyle changes can also help prevent the development of fungal acne. These changes include:
1. Avoiding Tight Clothing
Wearing tight clothing can trap sweat and create a favorable environment for the growth of yeast on the skin. To prevent this, wear loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics.
2. Avoiding Hot Showers
Hot showers can dry out the skin and create a favorable environment for the growth of yeast on the skin. To prevent this, take lukewarm showers instead.
3. Using Fragrance-Free Products
Fragrance-free products are less likely to irritate the skin and create a favorable environment for the growth of yeast on the skin. To prevent this, use fragrance-free skincare and laundry products.
4. Keep your skin clean and dry
Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, so it is important to keep your skin clean and dry. Avoid using heavy moisturizers or oils on the affected areas, and try to shower or bathe as soon as possible after sweating.
5. Avoid sharing personal items
Fungal infections can be spread through contact with contaminated items like towels, clothing, or makeup brushes. Avoid sharing these items with others, and wash them regularly to prevent the growth of fungi.
6. Maintain a healthy diet
A diet high in sugar and processed foods can contribute to the growth of fungi on the skin. Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet can help support a healthy immune system and prevent fungal acne.
Conclusion
Fungal acne is a common skin condition that is caused by an overgrowth of yeast on the skin. Understanding the causes and solutions for this skin disorder is crucial in preventing and treating this condition.
Mild cases of it can be treated with over-the-counter antifungal products, while more severe cases may require prescription medications. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can also help reduce the symptoms of fungal acne and prevent its development.
If you suspect that you have this kind of acne, it is important to consult with a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Don’t let fungal acne take over – take control of your skin health today.




